Free IRS Schedule C 1040 Template
The IRS Schedule C 1040 form is a critical document for individuals operating a business as a sole proprietorship. This form allows self-employed individuals to report their income and expenses, providing a clear picture of their business's financial health. On Schedule C, taxpayers detail their gross receipts, which include all revenue generated from their business activities. They also list various business expenses, such as costs for supplies, equipment, and travel, which can significantly impact their taxable income. Understanding how to accurately complete this form is essential, as it not only affects tax liability but also plays a role in determining eligibility for certain credits and deductions. Additionally, the form requires information about the business, including its name, address, and principal business activity, ensuring that the IRS has a comprehensive understanding of the taxpayer's operations. Completing Schedule C correctly can lead to potential tax savings, while errors can result in audits or penalties. For anyone engaged in self-employment, mastering the nuances of this form is a vital step in managing their financial responsibilities effectively.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Schedule C (Form 1040) is used by sole proprietors to report income or loss from their business. |
| Filing Requirement | If you have a business and earn a profit, you must file Schedule C along with your personal income tax return. |
| Business Expenses | Schedule C allows you to deduct various business expenses, which can reduce your taxable income. |
| Net Profit or Loss | The form calculates your net profit or loss, which is then transferred to your Form 1040. |
| Self-Employment Tax | Income reported on Schedule C may also subject you to self-employment tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare. |
| State-Specific Forms | Some states require additional forms for business income, governed by state tax laws, such as California's Form 540 or New York's IT-201. |
Similar forms
- Form 1040: This is the standard individual income tax return form used by taxpayers to report their annual income. Schedule C is attached to Form 1040 for reporting business income and expenses.
- Schedule SE: This form is used to calculate self-employment tax. If you report income on Schedule C, you will likely need to file Schedule SE as well.
- Form 1065: This is used by partnerships to report income, deductions, gains, and losses. Like Schedule C, it provides a detailed account of business activities.
- Form 1120: Corporations use this form to report income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits. It serves a similar purpose as Schedule C but for corporate entities.
- Form 1120-S: This form is for S corporations to report income, deductions, and credits. It parallels Schedule C in that it captures business financial details.
- Schedule E: Used for reporting supplemental income and loss, this form is similar in that it details income from rental properties and partnerships.
- Form 4562: This form is for depreciation and amortization. If a business has significant assets, it may need to attach this to Schedule C to account for asset depreciation.
- Form 8829: This form is used to calculate expenses for business use of your home. If applicable, it can be filed alongside Schedule C to detail home office deductions.
- Form 2106: This form is for employee business expenses. While it serves employees rather than self-employed individuals, it shares similarities in tracking business-related costs.
- Ohio Medical Power of Attorney: This important form enables individuals to appoint someone to make healthcare choices on their behalf. Access the essential Medical Power of Attorney document to secure your medical preferences.
- Form 941: This is used to report income taxes, Social Security tax, or Medicare tax withheld from employee's paychecks. While it is for employers, it relates to business operations similar to Schedule C.
IRS Schedule C 1040 Example
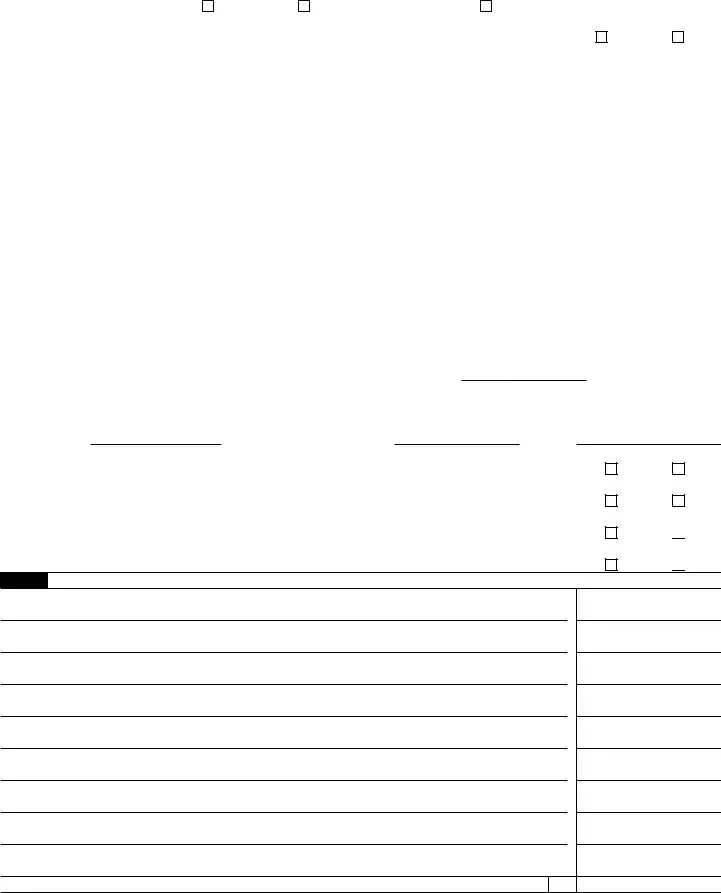
SCHEDULE C |
|
Profit or Loss From Business |
|
OMB No. |
|||||||
|
|
||||||||||
(Form 1040) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
(Sole Proprietorship) |
|
2020 |
|
|||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/ScheduleC for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
Attachment |
|||||||
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
▶ Attach to Form 1040, |
Sequence No. 09 |
||||||||
Name of proprietor |
|
|
|
Social security number (SSN) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
A |
Principal business or profession, including product or service (see instructions) |
|
B Enter code from instructions |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
C |
Business name. If no separate business name, leave blank. |
D Employer ID number (EIN) (see instr.) |
|||||||||
EBusiness address (including suite or room no.) ▶ City, town or post office, state, and ZIP code
F |
Accounting method: |
(1) |
Cash |
(2) |
Accrual |
(3) |
Other (specify) ▶ |
G |
Did you “materially participate” in the operation of this business during 2020? If “No,” see instructions for limit on losses . |
||||||
H |
If you started or acquired this business during 2020, check here . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶ |
|||||
I |
Did you make any payments in 2020 that would require you to file Form(s) 1099? See instructions |
||||||
J |
If “Yes,” did you or will you file required Form(s) 1099? |
||||||

 Yes
Yes  No
No

 Yes
Yes 
 No
No

 Yes
Yes  No
No
Part I Income
1 |
Gross receipts or sales. See instructions for line 1 and check the box if this income was reported to you on |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Form |
. . . . . . . . |
. ▶ |
1 |
|
|||||||||
2 |
Returns and allowances |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
|
2 |
|
|||||||||
3 |
Subtract line 2 from line 1 |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
|
3 |
|
|||||||||
4 |
Cost of goods sold (from line 42) |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
|
4 |
|
|||||||||
5 |
Gross profit. Subtract line 4 from line 3 |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
|
5 |
|
|||||||||
6 |
Other income, including federal and state gasoline or fuel tax credit or refund (see instructions) . . . . |
6 |
|
|||||||||||
7 |
Gross income. Add lines 5 and 6 |
. . . . . . . . |
. |
. ▶ |
7 |
|
||||||||
Part II |
Expenses. Enter expenses for business use of your home only on line 30. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
8 |
Advertising |
8 |
|
|
18 |
Office expense (see instructions) |
18 |
|
||||||
9 |
Car and truck expenses (see |
|
|
|
19 |
Pension and |
19 |
|
||||||
|
instructions) |
9 |
|
|
20 |
Rent or lease (see instructions): |
|
|
||||||
10 |
Commissions and fees . |
10 |
|
|
a |
Vehicles, machinery, and equipment |
20a |
|
||||||
11 |
Contract labor (see instructions) |
11 |
|
|
b |
Other business property . . . |
20b |
|
||||||
12 |
Depletion |
12 |
|
|
21 |
Repairs and maintenance . . . |
21 |
|
||||||
13 |
Depreciation and section 179 |
|
|
|
22 |
Supplies (not included in Part III) . |
22 |
|
||||||
|
expense deduction (not |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
23 |
Taxes and licenses |
23 |
|
|||||||
|
included in Part III) (see |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
instructions) |
13 |
|
|
24 |
Travel and meals: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
14 |
Employee benefit programs |
|
|
|
a |
Travel |
24a |
|
||||||
|
(other than on line 19) . . |
14 |
|
|
b |
Deductible meals (see |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
15 |
Insurance (other than health) |
15 |
|
|
|
instructions) |
24b |
|
||||||
16 |
Interest (see instructions): |
|
|
|
25 |
Utilities |
25 |
|
||||||
a |
Mortgage (paid to banks, etc.) |
16a |
|
|
26 |
Wages (less employment credits) . |
26 |
|
||||||
b |
Other |
16b |
|
|
27a |
Other expenses (from line 48) . . |
27a |
|
||||||
17 |
Legal and professional services |
17 |
|
|
b |
Reserved for future use . . . |
27b |
|
||||||
28 |
Total expenses before expenses for business use of home. Add lines 8 through 27a . . . . |
. |
. ▶ |
28 |
|
|||||||||
29 |
Tentative profit or (loss). Subtract line 28 from line 7 |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
|
29 |
|
|||||||||
30 |
Expenses for business use of your home. Do not report these expenses elsewhere. Attach Form 8829 |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
unless using the simplified method. See instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Simplified method filers only: Enter the total square footage of (a) your home: |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
and (b) the part of your home used for business: |
|
|
|
|
. Use the Simplified |
|
|
||||||
|
Method Worksheet in the instructions to figure the amount to enter on line 30 |
30 |
|
|||||||||||
31 |
Net profit or (loss). Subtract line 30 from line 29. |
|
|
|
|
|
} |
|
|
|
||||
|
• If a profit, enter on both Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 3, and on Schedule SE, line 2. (If you |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
checked the box on line 1, see instructions). Estates and trusts, enter on Form 1041, line 3. |
|
|
31 |
|
|||||||||
|
• If a loss, you must go to line 32. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
32 |
If you have a loss, check the box that describes your investment in this activity. See instructions. |
|
} |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
• If you checked 32a, enter the loss on both Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 3, and on Schedule |
|
|
32a |
All investment is at risk. |
|||||||||
|
SE, line 2. (If you checked the box on line 1, see the line 31 instructions). Estates and trusts, enter on |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
32b |
Some investment is not |
||||||||||
|
Form 1041, line 3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
at risk. |
|||
|
• If you checked 32b, you must attach Form 6198. Your loss may be limited. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the separate instructions. |
|
|
Cat. No. 11334P |
|
|
|
|
Schedule C (Form 1040) 2020 |
||||||

Schedule C (Form 1040) 2020 |
Page 2 |
|
Part III |
Cost of Goods Sold (see instructions) |
|
33 |
Method(s) used to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
value closing inventory: |
a |
Cost |
b |
Lower of cost or market |
c |
Other (attach explanation) |
34Was there any change in determining quantities, costs, or valuations between opening and closing inventory?
If “Yes,” attach explanation |
Yes |
No
35 |
Inventory at beginning of year. If different from last year’s closing inventory, attach explanation . . . |
35 |
|
|||
36 |
Purchases less cost of items withdrawn for personal use |
36 |
|
|||
37 |
Cost of labor. Do not include any amounts paid to yourself |
37 |
|
|||
38 |
Materials and supplies |
38 |
|
|||
39 |
Other costs |
39 |
|
|||
40 |
Add lines 35 through 39 |
40 |
|
|||
41 |
Inventory at end of year |
41 |
|
|||
42 |
Cost of goods sold. Subtract line 41 from line 40. Enter the result here and on line 4 |
42 |
|
|||
Part IV |
Information on Your Vehicle. Complete this part only if you are claiming car or truck expenses on line 9 |
|||||
|
|
and are not required to file Form 4562 for this business. See the instructions for line 13 to find out if you must |
||||
|
|
file Form 4562. |
|
|
|
|
43 |
When did you place your vehicle in service for business purposes? (month/day/year) |
▶ |
/ |
/ |
|
|
44Of the total number of miles you drove your vehicle during 2020, enter the number of miles you used your vehicle for:
a |
Business |
b Commuting (see instructions) |
c Other |
|
45 |
Was your vehicle available for personal use during |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . |
Yes |
|
46 |
Do you (or your spouse) have another vehicle available for personal use?. |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . |
Yes |
|
47a |
Do you have evidence to support your deduction? |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . |
Yes |
|
b |
If “Yes,” is the evidence written? |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . |
Yes |
|
Part V Other Expenses. List below business expenses not included on lines
No
No

 No
No

 No
No
48 Total other expenses. Enter here and on line 27a . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
48
Schedule C (Form 1040) 2020
Understanding IRS Schedule C 1040
What is IRS Schedule C?
IRS Schedule C is a form used by sole proprietors to report income or loss from a business they operate. It is filed along with Form 1040, the individual income tax return. The information on Schedule C helps determine the net profit or loss from the business, which is then included in the overall income reported on Form 1040.
Who needs to file Schedule C?
Individuals who operate a sole proprietorship must file Schedule C. This includes freelancers, independent contractors, and small business owners. If you earn income from self-employment, you are generally required to report it using this form.
What types of income should be reported on Schedule C?
All income earned from your business activities should be reported on Schedule C. This includes sales revenue, fees for services, and any other business-related income. It is important to keep accurate records of all income to ensure proper reporting.
What expenses can be deducted on Schedule C?
Common deductible expenses include costs related to supplies, advertising, travel, and home office expenses. You can also deduct business-related vehicle expenses, utilities, and wages paid to employees. Proper documentation of these expenses is essential for accurate reporting.
How do I calculate my net profit or loss on Schedule C?
To calculate your net profit or loss, subtract your total business expenses from your total business income. If your income exceeds your expenses, you have a profit. If your expenses are greater than your income, you have a loss. This figure is then transferred to your Form 1040.
Can I file Schedule C electronically?
Yes, Schedule C can be filed electronically using tax software or through a tax professional. Electronic filing is generally faster and may help reduce errors. Many tax software programs will guide you through the process of completing Schedule C.
What if I have a loss on my Schedule C?
If you report a loss on Schedule C, it can offset other income on your tax return, potentially reducing your overall tax liability. However, if you have losses for several consecutive years, the IRS may scrutinize your business to determine if it is a legitimate venture.
Are there any special considerations for home-based businesses?
Home-based businesses can deduct certain expenses related to the home office, such as a portion of rent or mortgage interest, utilities, and repairs. To qualify for these deductions, the home office must be used regularly and exclusively for business purposes.
Where can I find more information about Schedule C?
Additional information about Schedule C can be found on the IRS website. The IRS provides detailed instructions and resources to help you understand how to complete the form accurately. You may also consider consulting a tax professional for personalized assistance.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS Schedule C (Form 1040), it's important to be thorough and accurate. Here are some key dos and don'ts to consider:
- Do ensure that your business income is reported accurately.
- Do keep detailed records of all business expenses.
- Do use the correct accounting method (cash or accrual).
- Do report any home office deductions if applicable.
- Don't forget to include any 1099 forms received.
- Don't mix personal and business expenses.
- Don't leave any sections blank; fill out all applicable fields.
Check out Common Templates
California Child Labor Laws - School commitments should be considered when detailing work hours on this form.
The process of filing a civil action in California requires strict adherence to specific guidelines, including the submission of essential documentation like the Civil Case Cover Sheet (form CM-010). By utilizing the resources available, such as the California PDF Forms, individuals can ensure that their forms are filled out correctly and submitted without delay, thereby facilitating a smoother judicial process.
Minor Travel Consent Letter - The form can clarify roles if a minor is traveling with extended family or friends.
