Free IRS Schedule B 941 Template
The IRS Schedule B (Form 941) plays a crucial role in the payroll tax reporting process for employers. This form is specifically designed for reporting the tax liability for Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as federal income tax withheld from employees' wages. Employers must complete Schedule B if they have a tax liability of $100,000 or more during a deposit period. The form helps the IRS track the timing of tax deposits, ensuring compliance with federal tax laws. Additionally, it provides a clear overview of an employer’s payroll tax obligations over a specific quarter. By detailing the payroll tax liabilities, Schedule B helps maintain transparency and accountability in the tax system. Understanding how to properly fill out this form is essential for employers to avoid penalties and ensure accurate reporting. Overall, Schedule B is a vital tool for managing payroll taxes effectively and remains a key component in the broader context of employer tax responsibilities.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Schedule B (Form 941) is used by employers to report their federal income tax withheld and their share of Social Security and Medicare taxes for employees. |
| Filing Frequency | This form must be filed quarterly, along with Form 941, which is the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return. |
| Eligibility | All employers who withhold federal income tax, Social Security tax, or Medicare tax from their employees must complete Schedule B if they meet certain thresholds. |
| State-Specific Laws | While Schedule B is a federal form, employers should also comply with state-specific tax laws, which may vary. For example, California employers must adhere to the California Revenue and Taxation Code. |
Similar forms
The IRS Schedule B (Form 941) is a document used by employers to report certain tax information related to their employees. It specifically details the employer's tax liability and is filed alongside Form 941, which is the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return. Here are seven other documents that share similarities with Schedule B, along with explanations of how they are alike:
- Form W-2: This form is used to report wages paid to employees and the taxes withheld from those wages. Like Schedule B, it provides critical information about tax liabilities and employee compensation.
- Form 940: This form is the Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return. It requires employers to report unemployment taxes, similar to how Schedule B reports payroll taxes, both serving to inform the IRS about tax obligations.
- Form 1099-MISC: Used to report payments made to independent contractors, this form also tracks payments and tax withholdings, much like how Schedule B tracks employee-related tax information.
- Form 941: The main form for reporting employment taxes, Schedule B is an attachment to Form 941. Both documents are essential for employers to report their payroll tax obligations accurately.
- Form 945: This form is used to report federal income tax withheld from nonpayroll payments. Similar to Schedule B, it serves as a reporting mechanism for tax withholdings but focuses on different types of payments.
- Form 1120: This is the U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return. While it is primarily for corporations, it also reports tax liabilities, akin to how Schedule B reports payroll-related tax obligations for employers.
- Ohio Lease Agreement Form: For those entering rental agreements, our thorough Ohio lease agreement documentation ensures all essential terms are clearly defined and legally compliant.
- Form 1065: Used by partnerships to report income, deductions, and other tax information, it shares a common purpose with Schedule B in that both forms help ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance.
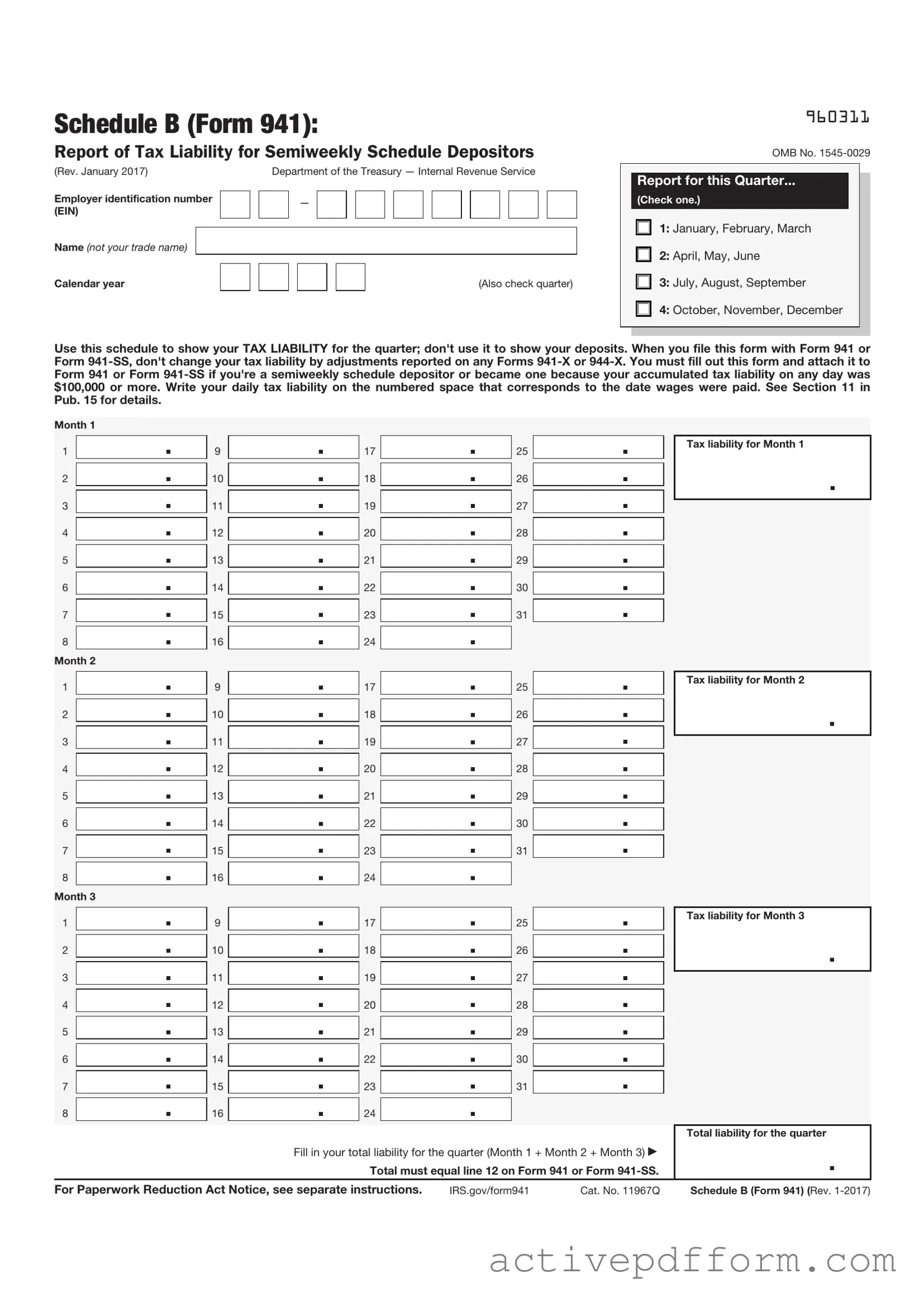
IRS Schedule B 941 Example

Schedule B (Form 941):
Report of Tax Liability for Semiweekly Schedule Depositors
(Rev. January 2017) |
|
|
Department of the Treasury — Internal Revenue Service |
|||||||||||||||||||
Employer identification number |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(EIN) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name (not your trade name) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calendar year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Also check quarter) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
960311
OMB No.
Report for this Quarter...
(Check one.)
1: January, February, March
2: April, May, June
3: July, August, September
4: October, November, December
Use this schedule to show your TAX LIABILITY for the quarter; don't use it to show your deposits. When you file this form with Form 941 or Form
Month 1
1 .
.
2 .
.
3 .
.
4 .
.
5 .
.
6 .
.
7 .
.
8 .
.
Month 2
1 .
.
2 .
.
3 .
.
4 .
.
5 .
.
6 .
.
7 .
.
8 .
.
Month 3
9 .
.
10 .
.
11 .
.
12 .
.
13 .
.
14 .
.
15 .
.
16 .
.
9 .
.
10 .
.
11 .
.
12 .
.
13 .
.
14 .
.
15 .
.
16 .
.
17 .
.
18 .
.
19 .
.
20 .
.
21 .
.
22 .
.
23 .
.
24 .
.
17 .
.
18 .
.
19 .
.
20 .
.
21 .
.
22 .
.
23 .
.
24 .
.
25 .
.
26 .
.
27 .
.
28 .
.
29 .
.
30 .
.
31 .
.
25 .
.
26 .
.
27 .
.
28 .
.
29 .
.
30 .
.
31 .
.
Tax liability for Month 1
.
Tax liability for Month 2
.
1 |
|
. |
9 |
|
. |
17 |
|
|
. |
25 |
|
. |
|
Tax liability for Month 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
2 |
|
. |
10 |
|
. |
18 |
|
|
. |
26 |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
. |
11 |
|
. |
19 |
|
|
. |
27 |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
. |
12 |
|
. |
20 |
|
|
. |
28 |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
. |
13 |
|
. |
21 |
|
|
. |
29 |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
. |
14 |
|
. |
22 |
|
|
. |
30 |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
. |
15 |
|
. |
23 |
|
|
. |
31 |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
. |
16 |
|
. |
24 |
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liability for the quarter |
|
|
|
|
Fill in your total liability for the quarter (Month 1 + Month 2 + Month 3) |
. |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total must equal line 12 on Form 941 or Form |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
IRS.gov/form941 |
Cat. No. 11967Q |
Schedule B (Form 941) (Rev. |
|||||||||||
Understanding IRS Schedule B 941
What is the IRS Schedule B (Form 941)?
The IRS Schedule B (Form 941) is a form that employers use to report their tax liabilities for federal income tax withholding and Social Security and Medicare taxes. It is specifically designed for employers who have a significant amount of payroll tax liability. This form provides a detailed breakdown of the employer's tax obligations for each quarter of the year. It is typically filed alongside Form 941, which is the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return.
Who needs to file Schedule B (Form 941)?
Employers who report a total tax liability of $100,000 or more during a deposit period must file Schedule B (Form 941). This includes those who have a large payroll or those who have had to make adjustments to their tax liabilities. Even if an employer does not owe taxes at the time of filing, they may still need to complete this schedule if they meet the liability threshold.
When is Schedule B (Form 941) due?
Schedule B (Form 941) is due on the same schedule as Form 941. Employers must file Form 941 quarterly, and the due dates are typically the last day of the month following the end of each quarter. For example, for the first quarter ending March 31, the form is due by April 30. It is essential to file on time to avoid penalties and interest on any unpaid taxes.
How do I complete Schedule B (Form 941)?
To complete Schedule B, employers need to provide information about their payroll tax liabilities. This includes the total amount of taxes owed for each month in the quarter. Employers will also need to indicate any adjustments made during the quarter. The form requires careful attention to detail, as inaccuracies can lead to penalties. It's advisable to refer to the instructions provided by the IRS for specific guidance on filling out the form correctly.
What happens if I don’t file Schedule B (Form 941) when required?
If an employer fails to file Schedule B (Form 941) when required, they may face significant penalties. The IRS can impose fines based on the amount of tax owed, and interest may accrue on any unpaid taxes. Additionally, failing to file can lead to further scrutiny from the IRS, which could result in audits or additional penalties. It is crucial for employers to stay compliant with all filing requirements to avoid these issues.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS Schedule B (Form 941), it is crucial to follow specific guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here’s a list of important dos and don’ts:
- Do double-check your EIN (Employer Identification Number) for accuracy.
- Do report all wages and tips accurately to avoid penalties.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records.
- Do file the form on time to prevent late fees.
- Do consult the IRS instructions if you have questions.
- Don't leave any fields blank; provide information for all required sections.
- Don't ignore discrepancies in reported amounts; resolve them before submission.
- Don't forget to sign and date the form before sending it.
- Don't submit the form without reviewing it for errors.
- Don't rely solely on software; manual verification is essential.
Check out Common Templates
Hunter Permission - Game species covered by the permission can be clearly listed on the form.
In addition to ensuring a seamless transfer, utilizing the California Boat Bill of Sale helps both parties maintain accurate records of their transactions, which can be crucial for future reference. For those looking to easily fill out this form, please visit California PDF Forms for a convenient solution.
Affidavit of Support - The I-864 can affect the sponsor’s ability to petition for additional family members in the future.